Since the first virus sent by email in 1999, technology has never stopped trying to catch up with cybercriminals' ingenuity and ability to renew treat tactics.
We have gathered for you the most important virus, trojan or ransomware who has spread mainly via emails. Note how attacks have varied even faster in the last 2 years!
Are you protected against latest ransomware threats?
How ransomware be like in 2022?
2020 marked a turning point with the COVID-19 pandemics and the increase of remote working for companies who had not adequate IT security measures in place. Ransomware attack raised not only among large corporate but also and mainly in small and medium businesses.
Volume ransomware are forecasted to continue growing in 2022 with the increase of social engineering attacks and ransomware-as-a-service, which packs are sold over for as less as US$50. Anyone can afford it and use it to spread already existing ransomware, or can develop new and more tenacious versions while giving a percentage of paid ransom to the organisations that initially sold them the RaaS kit. It's only benefit for both "old" cybercriminals, "new ones"...but of course, not for any organisation and home-users.
How to protect against next generation ransomware?
A Cloud Email Security Gateway (ESG) will filter and scan all emails in the Cloud before it reaches your email server, removing any possible threats. The more filter and engines, the better.
If you are searching for an effective ESG solution, we block ransomware, phishing attacks, detect Business Email Compromise and fraud contained in email, attachments and URLs contained in email messages. Our solution is located in the Cloud, before your email server.
Check our Email Security service with no compromise
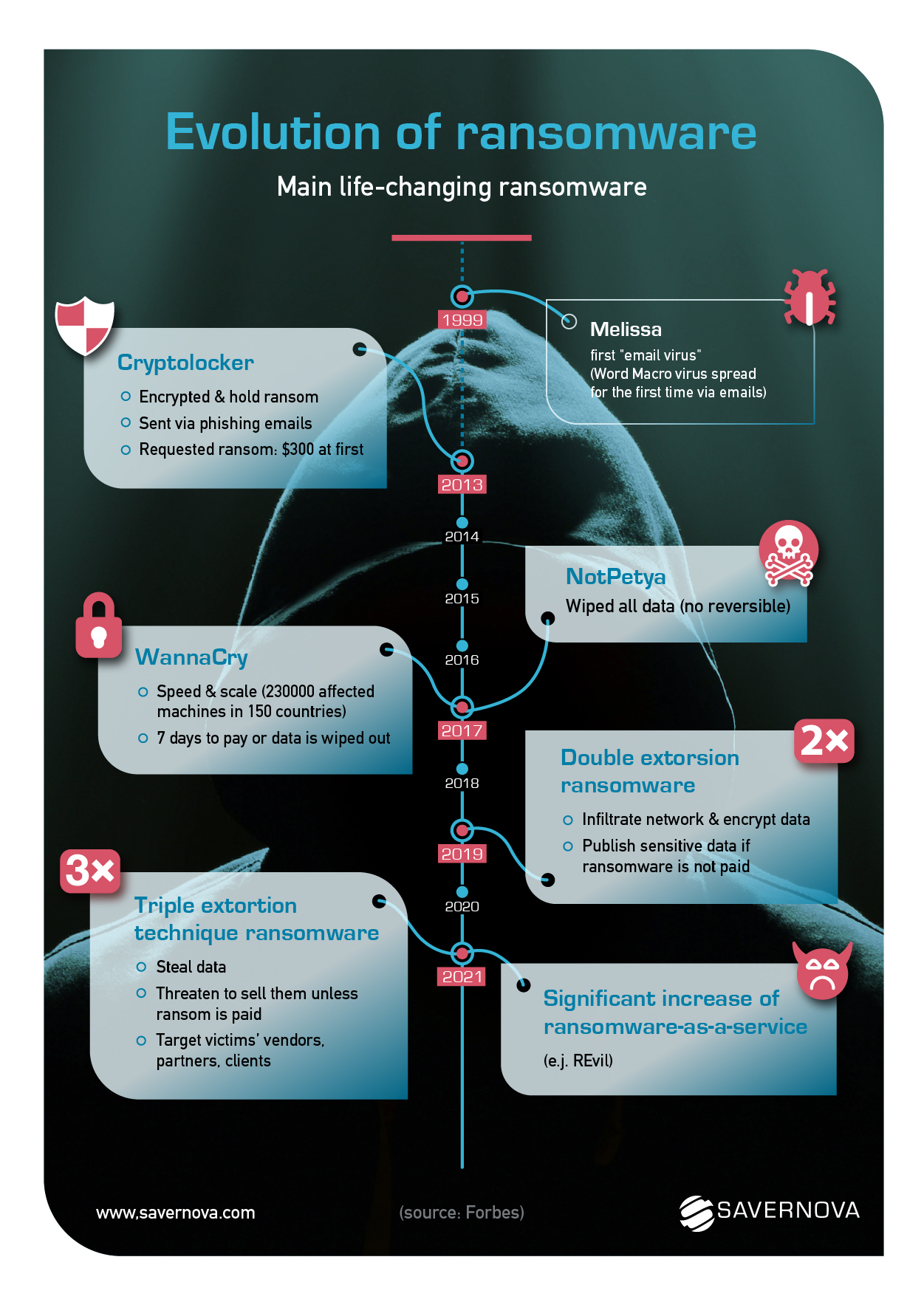
Main life-changing email virus, mailware, ransomware
1999: Melissa
First virus sent by emails
2013: CryptoLocker
- Encrypted & hold ransom
- Sent via phishing emails
- Requested ransom: $300 at first
2017: Wannacry
- Speed & scale (230000 affected machines in 150 countries)
- 7 days to pay or data is wiped out
2017: NotPetya
Wiped all data (no reversible)
2019: Double extorsion ransomware
- Infiltrate network & encrypt data
- Publish sensitive data if ransomware is not paid
2021: Significant increase of ransomware-as-a-service (e.j. REvil)
2021: Triple extortion technique ransomware
- Steal data
- Threaten to sell them unless ransom is paid
- Target victims’ vendors, partners, clients
 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch